



Next: 5.9 Single Detector Signal
Up: 5 Instrumental Characteristics
Previous: 5.7 Effects of pointing
This section discusses investigations of the grating instrumental profile and
describes possible instrumental effects on emission lines profiles
observed with SWS.
Ground-based tests showed these Instrumental Profiles (IPs) to have a Gaussian
shape up to accuracies of a few percent. To verify that this would also be
the case in-flight, several objects showing strong, narrow, emission lines
(mostly Planetary Nebulae) were observed in ISO's performance verification
(PV ) phase to investigate the influence of parameters such as the
position of the source in the aperture, the size of the target and the SWS AOT
band.
These measurements were based on AOT 2 and 6 observations, but should also be
applicable to AOT 7 SW grating observation. AOT 1 measurements were discussed
in section 4.2.3.
Table 5.3 lists the objects used to derive the IP for AOTs 2 and 6.
Preliminary results of the tests on the position of the source in the
aperture can be summarised as follows: changes in the instrumental profile
from Gaussian become noticeable with an offset of a few arcseconds. The
shape, central wavelength and the line strength can vary drastically as the
source moves further away from the aperture center. This is illustrated in
Fig. 5.13, showing the line profiles and object positions wrt the
slit.
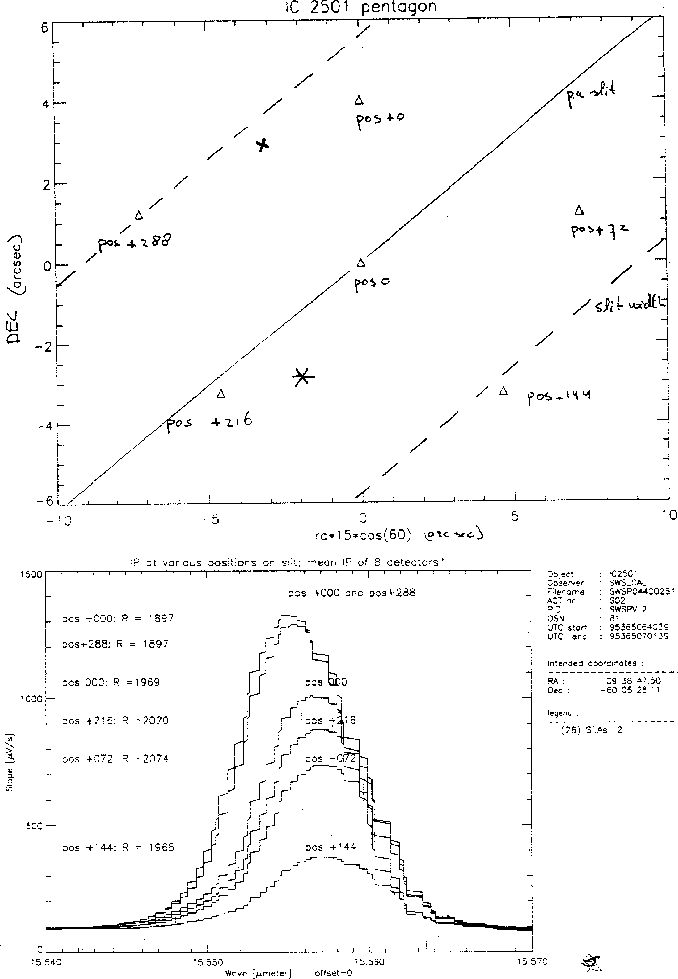
Figure 5.13: Changes in SWS instrumental profile and resolving power R
with the position of the source in the slit.
The effect of target size, central wavelength and scanning direction on
the IP was investigated using a large number of high S/N AOT S02 and S06
PV observations in all AOT bands of sources expected to show strong
unresolved emission lines. Details of the observations used for this study
are listed in Table 5.3. Since these data were generally taken
for other purposes, these should provide a good test for what can be expected
during real observations. For each measured emission line we applied some
minimal reduction steps, after which the resulting line profile was plotted
and compared to a Gaussian fitted to the data. Several examples of such line
profiles are shown in Figures 5.14 and 5.15.
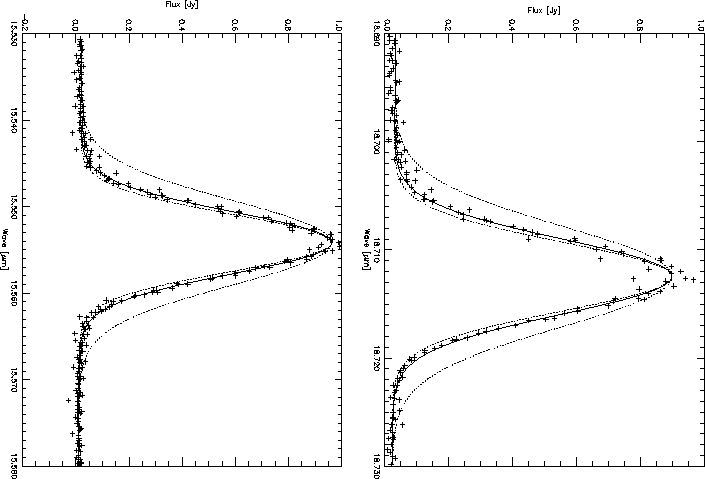
Figure 5.14: Examples of measured SWS lines (crosses) for extended sources. The
measured IPs are compared to a Gaussian fit to the data (solid line), a
Gaussian with the expected resolving power for a point source (lower dotted
line) and a Gaussian with the expected resolving power for an extended source
(upper dotted line).
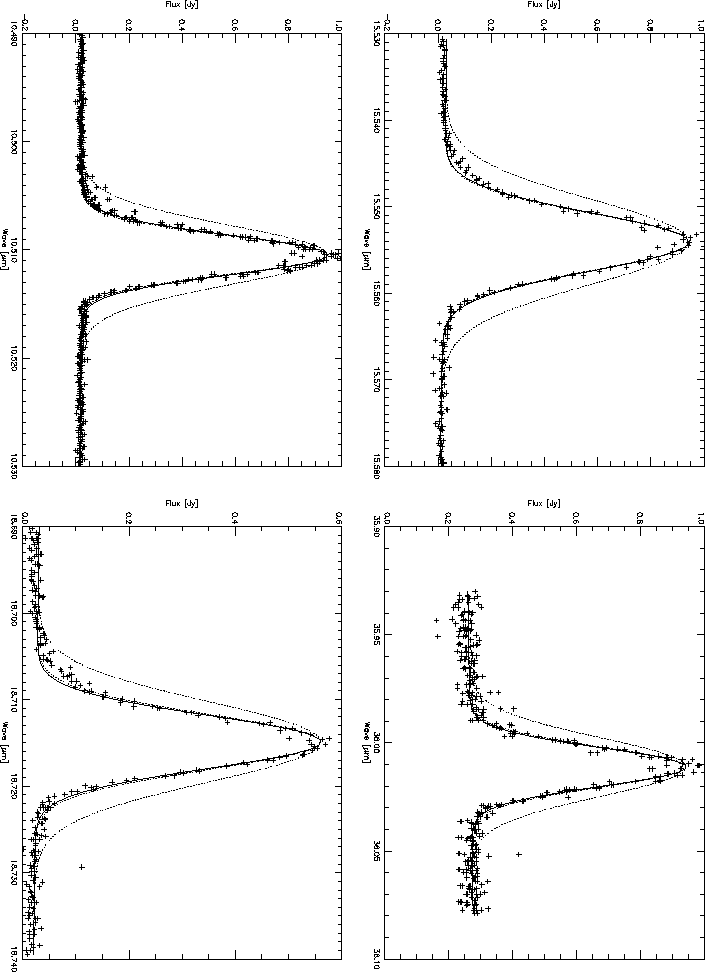
Figure 5.15: Examples of measured SWS lines (crosses) for unresolved sources. The
measured IPs are compared to a Gaussian fit to the data (solid line), a
Gaussian with the expected resolving power for a point source (lower dotted
line) and a Gaussian with the expected resolving power for an extended source
(upper dotted line).
As can be seen from figures 5.14 and 5.15, the peak of
the profiles closely follow a Gaussian shape. At 10% above continuum some
deviations from the Gaussian shape start to become visible - there always
seems to be an indentation on the red side and a bump on the blue side. These
deviations, most visible in the more point-like sources and well within the few
percent deviations already noted pre-launch, are present in all AOT bands and,
as far as it has been possible to determine due to the different noise levels,
also present in all detectors. They are also present and identical in the up-
and down-scans. Interestingly, these deviations from Gaussian look like a
less extreme version of those seen when offsetting the source in the slit
(Fig. 5.13). Since only a small number of sources (although a large
number of measurements), largely measured in the same orbits, were used in the
determination of the IPs, they could be due to a systematic small (well within
the pointing specifications) pointing offset for these sources. Determinations
of IPs for more sources, observed during more orbits are necessary to get more
insight in this.
As expected, extended sources show a broader instrumental profile than the
more point-like sources. As is illustrated in Figure 5.14, a
Gaussian can also adequately reproduce these profiles and, although less so
than in the point-like sources, the same asymmetry at the shoulders of the
profile can be seen here.
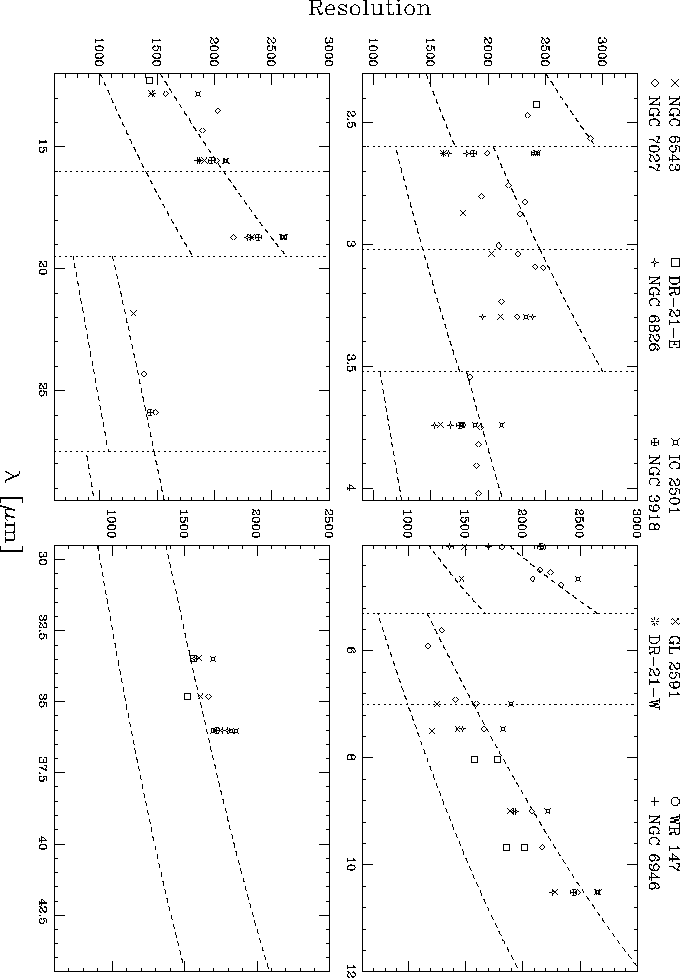
Figure 5.16: Measured SWS resolving power  as a function of
wavelength for different sources. The dotted lines indicate the resolving
power for a point source (upper line) and a fully extended source (lower
line), as given by the IA resolution module, which computes this value from
the combined effects of diffraction, slit width, source size, ISO jitter and
detector size.
as a function of
wavelength for different sources. The dotted lines indicate the resolving
power for a point source (upper line) and a fully extended source (lower
line), as given by the IA resolution module, which computes this value from
the combined effects of diffraction, slit width, source size, ISO jitter and
detector size.
The resolving power  was measured from the observed
instrumental profiles. A plot of these values of R against wavelength for
all measured lines is shown in Fig. 5.13. Typical errors in R are
a few hundred, depending on the line strength and achieved S/N ratio. Errors
in
was measured from the observed
instrumental profiles. A plot of these values of R against wavelength for
all measured lines is shown in Fig. 5.13. Typical errors in R are
a few hundred, depending on the line strength and achieved S/N ratio. Errors
in  are much smaller than the plot symbols. From Fig. 5.16
we note that none of the points seem to be close to the expected values for
fully extended sources, although several sources that are expected to
completely fill the SWS aperture were also included in the study. It is
possible the assumption they are extended is not valid because the
line-emission in the Planetary Nebulae used for this purpose could come from a
smaller region that the continuum radiation. In SWS bands 2 to 4 we note that
a significant fraction of the measured points are located at higher resolutions
than expected for a point source. Therefore we conclude that the resolving
power of the SWS grating must be better than predicted in these wavelength
regimes.
are much smaller than the plot symbols. From Fig. 5.16
we note that none of the points seem to be close to the expected values for
fully extended sources, although several sources that are expected to
completely fill the SWS aperture were also included in the study. It is
possible the assumption they are extended is not valid because the
line-emission in the Planetary Nebulae used for this purpose could come from a
smaller region that the continuum radiation. In SWS bands 2 to 4 we note that
a significant fraction of the measured points are located at higher resolutions
than expected for a point source. Therefore we conclude that the resolving
power of the SWS grating must be better than predicted in these wavelength
regimes.
The main conclusions are summarised below. It should be remembered that they
are based on AOT 2 & 6 observations, should be applicable to AOT 7 SW grating
observations but are not applicable to AOT 1 observations.
- The SWS grating instrumental profile is very close to Gaussian.
- The only systematic differences from a Gaussian profile are a
slight ``shoulder'' on the blue side of the base of the profile and a
depression on the red side as compared to a purely Gaussian profile.
The only parameter this seems to depend on is the position of the source
in the slit.
- The grating resolving power of SWS for all investigated sources is better
than expected for extended sources at all wavelengths. This could either mean
that none of line-emitting regions in any of the sources fully filled
the SWS aperture, or that the SWS resolving power for extended sources is
better than expected.
- In AOT bands 2 to 4 the resolving power for point-like sources is
slightly better than predicted from the ground.




Next: 5.9 Single Detector Signal
Up: 5 Instrumental Characteristics
Previous: 5.7 Effects of pointing
K. Leech with contributions from
the SWS Instrument Dedicated Team (SIDT)
and the SWS Instrument Support Team (SIST)



